Effects of Caffeine on Human body
Caffeine is a natural stimulant most commonly found in tea, coffee and cacao plants.
Health News : Many of us rely on a morning cup of coffee or a jolt of caffeine in the afternoon to help us get through the day. But caffeine does so much more than just keeping you awake. It’s a central nervous system stimulant that affects your body in numerous ways.
Caffeine provides no nutritional value on its own. It’s tasteless, so you won’t necessarily know if it’s in your food either. Even some medications may contain caffeine without your knowledge.
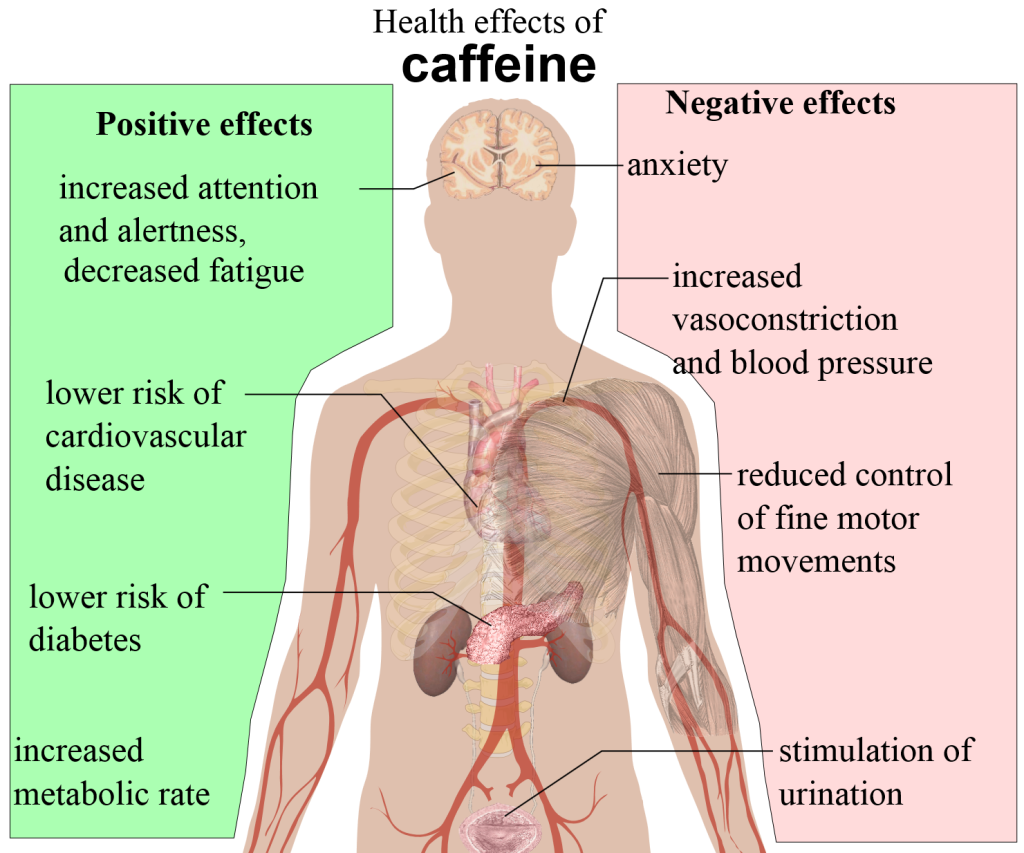
At a minimum, you may feel more energetic, but over time, too much caffeine may cause withdrawal symptoms. Caffeine acts as a central nervous system stimulant. When it reaches your brain, the most noticeable effect is alertness. Studies have also found that people who drink coffee regularly have a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s and dementia, and cut suicide risk by 45%.
These benefits are limited to people who drink high-octane coffee, not decaf. Extra caffeine doesn’t get stored in your body either. It’s processed in the liver and exits through your urine. Caffeine can make your blood pressure go up for a short time. If you consume too much, caffeine may cause also your muscles to twitch.
An overdose of caffeine may cause rapid or irregular heartbeat and breathing trouble. In rare cases, caffeine overdose can result in death due to convulsions or irregular heartbeat.
How it Works
Once consumed, caffeine is quickly absorbed from the gut into the bloodstream. From there, it travels to the liver and is broken down into compounds that can affect the function of various organs.
That said, caffeine’s main effect is on the brain. It functions by blocking the effects of adenosine, which is a neurotransmitter that relaxes the brain and makes you feel tired.
Normally, adenosine levels build up over the day, making you increasingly more tired and causing you to want to go to sleep. Caffeine helps you stay awake by connecting to adenosine receptors in the brain without activating them. This blocks the effects of adenosine, leading to reduced tiredness.
It may also increase blood adrenaline levels and increase brain activity of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine. This combination further stimulates the brain and promotes a state of arousal, alertness, and focus. Because it affects your brain, caffeine is often referred to as a psychoactive drug.
Additionally, caffeine tends to exert its effects quickly. For instance, the amount found in one cup of coffee can take as little as 20 minutes to reach the bloodstream and about 1 hour to reach full effectiveness.

No comments:
Post a Comment